Medical credentialing is vital for ensuring that healthcare professionals are qualified to provide high-quality care and minimize malpractice risks. This process involves verifying a healthcare professional’s education, training, licensure, board certifications, and work history. It is a critical step in healthcare credentialing that ensures the safety and efficacy of medical care.
To participate in Medicare, healthcare providers must have an NPI number and complete an application that includes information about their credentials, licensure, and experience. Additionally, healthcare providers must be registered with their state Medicaid agency and meet specific state credentialing requirements to join the Medicaid program.
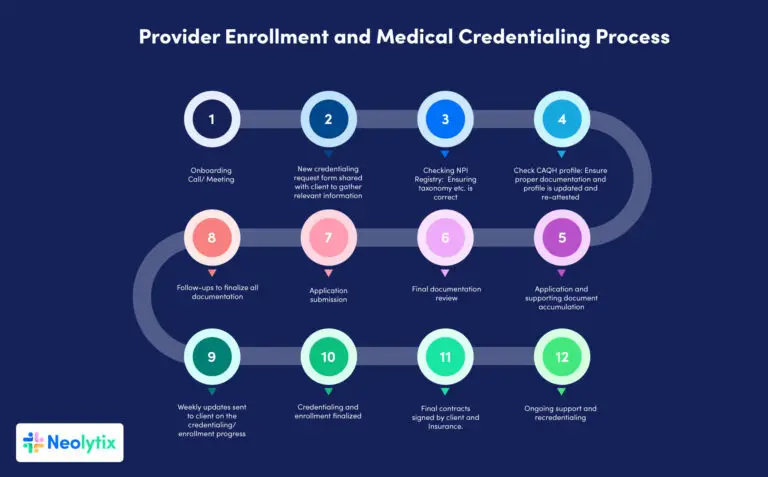
Given the complexity of the credentialing process for providers, it’s essential to adopt efficient practices. Here are seven steps to help improve the medical credentialing process, making it less time-consuming and more effective:
7 Steps to Improve the Medical Credentialing Process
Credentialing in healthcare can be time-consuming and frustrating. To streamline the provider credentialing process and improve efficiency, follow these seven steps carefully:
1. Identify the Required Credentials
Understanding and identifying the necessary credentials is crucial in ensuring healthcare professionals meet the qualifications for their roles. This process involves determining the specific education, training, licensure, and other requirements needed to practice in your healthcare organization.
Common qualifications and credentials include:
- Education: Degrees from accredited medical schools
- Training: Completion of residency programs
- Licensure: State medical licenses
- Board Certifications: Certification in relevant specialties
- Work History: Previous employment verification
Ensuring these credentials are accurately identified helps maintain the high standards of care within your organization.
2. Gather Necessary Information
Collect all required documentation and verify the healthcare professional’s work history, licensure, education, and board certifications. Having complete and accurate information is essential for a successful credentialing process in healthcare.
3. Verify Primary Sources
Checking primary sources is crucial for verifying the accuracy and reliability of a healthcare professional’s information during credentialing. It involves obtaining information directly from primary sources such as licensing boards, medical schools, and previous employers.
4. Use a Centralized System
A centralized system for the medical credentialing process ensures all necessary documents are received on time and deadlines are met. It provides a streamlined approach to managing the entire process and allows for efficient communication between all parties involved.
5. Adopting Technology
Incorporating technology can automate parts of the credentialing process, reducing the time required. Electronic verification of licensure and board certifications, for example, can significantly speed up the provider credentialing process steps.
6. Prioritize the Process
Giving the credentialing process the necessary attention and resources ensures it is not delayed by competing priorities. Prioritizing the process helps it be completed promptly and efficiently.
7. Follow Up Regularly
Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers and relevant parties are crucial for maintaining smooth communication and addressing any issues quickly. This step is often overlooked, leading to delays in the credentialing workflow. Additionally, regular check-ins are important for communication. They help resolve issues quickly and keep the process on track.
For many healthcare organizations, this step is the biggest culprit when it comes to delays. Office workers are too busy with their tasks. They cannot also be responsible for scheduling and conducting regular check-ups like police officers.
Read More: Credentialing 101 Guide for Therapists
Overcoming Common Credentialing Issues in Healthcare
The credentialing process for providers is crucial for maintaining high standards in medical care. Addressing common credentialing issues in healthcare can streamline the process and ensure healthcare professionals are properly vetted.
Credentialing in Medical Billing
Ensuring accurate documentation is vital in the credentialing process in medical billing. This impacts the provider’s ability to offer services and affects reimbursement. Utilizing technology and a centralized system can expedite provider credentialing in medical billing, reducing errors and delays.
Types of Credentialing in Healthcare
There are various types of credentialing in healthcare, tailored to different roles. This includes credentialing for physicians, nurses, allied health professionals, and medical assistants. Understanding specific provider credentialing requirements for each role ensures comprehensive credentialing.
The following types of credentialing are essential for ensuring that healthcare providers are qualified and competent, ultimately protecting patient safety and maintaining high standards of care.
- Primary Source Verification (PSV): This involves directly verifying a practitioner’s credentials with the issuing institutions, such as medical schools, residency programs, and licensing boards.
- Hospital Privileging: This process grants practitioners the authority to perform specific procedures and services within a hospital. It involves a thorough review of the practitioner’s qualifications, experience, and competency.
- Board Certification: This is a voluntary process where physicians demonstrate their expertise in a specific medical specialty by passing rigorous exams and fulfilling continuing education requirements.
- State Licensing: Each state requires healthcare providers to obtain a license to practice. This process includes verifying education, training, and passing relevant exams.
- Health Plan Credentialing: Health insurance companies conduct this type of credentialing to ensure providers meet their standards before being included in their network. It involves verifying qualifications, reviewing malpractice history, and assessing overall competency.
The Step-by-Step Credentialing Process
A defined step-by-step credentialing process is essential to ensure healthcare providers meet all necessary qualifications and standards. Here is an overview of the key steps involved:
Initial Application Review
Collect and review the initial application to ensure all required information is included. This includes personal details, educational background, training, work history, and references.
Primary Source Verification (PSV)
Verify credentials directly with the issuing institutions, such as medical schools, residency programs, and licensing boards. This step confirms the authenticity of the applicant’s qualifications.
Secondary Review
Conduct a thorough secondary review to identify any discrepancies or missing information from the initial application. This may involve cross-referencing details and following up on any inconsistencies.
Committee Review
Present the application and verification results to a credentialing committee for final approval. The committee typically includes experienced healthcare professionals who assess the applicant’s qualifications, experience, and competency.
Ongoing Monitoring
Continuously monitor the provider’s credentials to ensure they remain current. This involves tracking license renewals, board certifications, and any disciplinary actions or malpractice claims.
Credentialing for Physicians and Other Providers
The physician credentialing process requires a comprehensive review of education, training, licensure, and board certifications. A physician credentialing checklist ensures all steps are followed. Similarly, credentialing for medical providers maintains high standards of care.
Integration and Compliance
Integrating the medical provider credentialing process with other systems, like medical billing, ensures compliance and efficiency. The credentialing process for doctors must align with billing practices to prevent reimbursement issues.
Summary
Outsourcing the medical credentialing process for providers process offers numerous advantages to healthcare organizations. It allows facilities to focus on patient care while ensuring the accuracy and efficiency of the credentialing process. By partnering with experts like Neolytix, organizations gain access to specialized knowledge and advanced technology, which streamline credentialing procedures.
With 12 years of experience in helping healthcare practices across the country with enrollment and credentialing challenges, Neolytix is a trusted partner. Our expertise in the provider credentialing process ensures that your practice can reach its full potential.
Contact us today to explore how we can optimize your provider credentialing process flow and improve your organization’s efficiency.
Schedule A Free Consultation Today
Medical Credentialing Quote (Active)
"*" indicates required fields
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Credentialing in Healthcare
Yes, credentialing is a critical part of the Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) process. Ensuring that healthcare providers are properly credentialed with payers allows practices to avoid reimbursement delays and denials.
This is particularly important for maintaining smooth billing cycles and maximizing revenue. A properly completed insurance credentialing process ensures that providers can bill for services rendered under different insurance plans, thus tying into the overall RCM strategy.
The professional provider credentialing process is a thorough verification of a healthcare provider’s qualifications, including education, training, licensure, and work history. This applies across various specialties, whether you're navigating the VA credentialing process or working through the physician credentialing process. In the case of mental health credentialing with insurance companies, the process ensures mental health providers meet payer requirements, which is vital for inclusion in insurance networks.
A credentialing checklist outlines all the necessary steps and documentation required for the medical credentialing process. It typically includes:
- Verification of education and training
- Insurance credentialing
- State licensure and certifications
- Board certification
Work history and professional references
This checklist helps practices streamline their provider credentialing process and avoid missing critical information.
It’s basically the method by which healthcare organizations verify the qualifications of their providers, including physicians, nurses, and other allied professionals. The physician credentialing process ensures that doctors are legally and professionally qualified to offer care, while credentialing mental health providers focuses on the specific requirements for mental health professionals. Overall, what is healthcare credentialing? It safeguards patient safety by ensuring that only qualified professionals provide medical services.
The primary purpose of credentialing in healthcare is to maintain high standards of care and reduce risks for patients. By verifying each provider’s qualifications, healthcare organizations can ensure that their staff is capable of delivering top-tier care. This is particularly important when partnering with insurance credentialing services that require providers to meet specific network standards.
Provider enrollment is crucial because it ensures that healthcare professionals can be reimbursed for services by payers. Without proper enrollment in insurance networks, even the most qualified providers would not be able to bill insurance companies. In turn, this would prevent patients from using their insurance benefits to cover medical costs.
Provider credentialing is vital for ensuring patient safety and operational efficiency. The professional provider credentialing process verifies a provider’s qualifications and ensures they meet industry standards. It also streamlines the insurance credentialing process, making sure providers can participate in payer networks and receive compensation for their services.
An example of credentialing would be the physicians credentialing process, where a doctor’s medical degree, residency training, board certification, and state licensure are verified before they are allowed to treat patients at a hospital or medical facility. In insurance credentialing, providers must meet payer standards before joining an insurance network, allowing them to bill for their services.
There are several types of credentialing in healthcare, depending on the provider’s role:
- Primary Source Verification (PSV): Verifying a provider’s education and licensure directly from the issuing institutions.
- Insurance Credentialing: Verifying that providers meet payer standards to join an insurance network.
- Hospital Privileging: Granting providers the authority to perform specific procedures in a hospital setting.
- Board Certification: Physicians voluntarily undergo this process to demonstrate expertise in their specialty.
- Mental Health Credentialing with Insurance Companies: Ensuring mental health providers meet insurance requirements to offer reimbursable services.
Each type ensures that healthcare providers meet both credentialing services and industry standards, enhancing the quality of care patients receive.
In the credentialing process, various aspects of a healthcare provider's qualifications are evaluated. This includes education, training, licensure, and board certifications, along with their work history and malpractice history. The goal of what is provider credentialing is to ensure that healthcare professionals are competent and qualified to deliver care. For organizations working with physician credentialing services, these evaluations are critical to maintaining a high standard of care and patient safety.
The are three primary methods that are used in the credentialing process:
- Primary Source Verification: This involves verifying qualifications directly from the issuing institutions, such as medical schools or licensing boards.
- Facility Credentialing: Hospitals and other healthcare facilities perform a hospital credentialing process to authorize providers to practice at their facility.
- Payer Credentialing: Insurance companies use payer credentialing to verify that providers meet their standards before allowing them to join their network, ensuring smooth reimbursement processes.
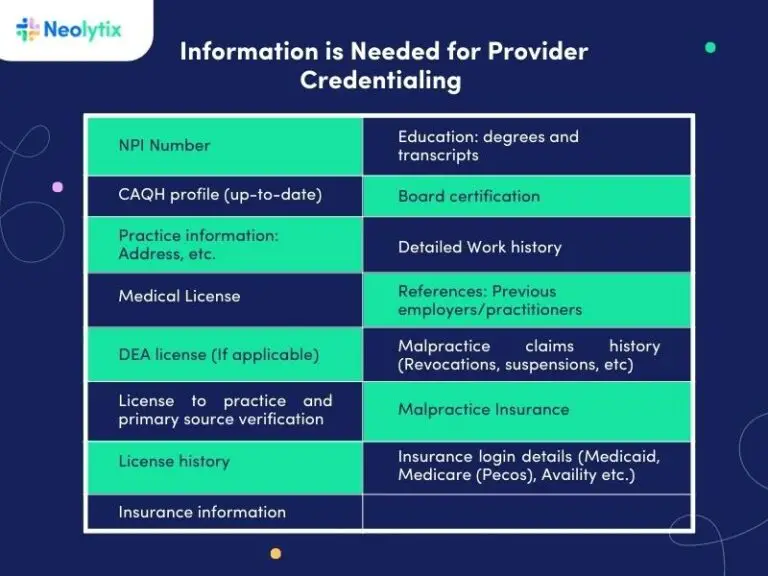
To complete the provider credentialing process, healthcare providers must submit several documents, including:
- State medical licenses
- DEA certificates
- Board certifications
- Educational transcripts
- Work history and references
Professional liability insurance These documents are required by provider credentialing companies and are also essential for insurance credentialing for providers. Whether for doctors or credentialing nurse practitioners, having these documents prepared and verified speeds up the process significantly.
Provider credentialing involves verifying a healthcare provider’s qualifications to ensure they meet the necessary standards to practice. On the other hand, provider enrollment is the process of getting a provider accepted by an insurance company or Medicare, allowing them to bill for services rendered. Both processes are essential, but provider credentialing verifies competency, while provider enrollment ensures that the provider can be reimbursed by payers like Medicare or private insurance.
Additionally, what is credentialing in medical billing refers to the credentialing process specifically related to enabling billing for medical services, further emphasizing the importance of both steps for operational and financial efficiency.
Outsourcing medical credentialing services to a trusted credential service provider offers numerous benefits, including:
- Reducing administrative burdens on your staff
- Speeding up the provider credentialing process
- Avoiding errors that could delay reimbursement
- Gaining access to experts familiar with payer requirements, such as insurance credentialing for nurse practitioners
- Ensuring timely renewals and updates to credentials, which is critical for healthcare credentialing services
For specialized providers, such as nurse practitioners and doctors, outsourcing doctor credentialing services can help avoid common pitfalls and streamline the onboarding process, ensuring a seamless workflow.
For Medicare provider enrollment, the following documents are typically required:
- National Provider Identifier (NPI)
- Medical licenses
- Proof of board certification
- Work history and references
- Copies of professional liability insurance This documentation helps ensure compliance with Medicare’s provider credentialing process and is vital for successful enrollment.
The time to complete Medicare provider enrollment can vary, but it typically takes between 60 to 90 days. For a streamlined process, healthcare providers often rely on physician credentialing services or credentialing services for providers to ensure that all documents are submitted accurately, reducing delays in approval. Providers may wonder how long does credentialing take in general, but timelines can vary depending on the complexity and the payer’s requirements.
The credentialing process generally involves several key steps:
- Collecting necessary documents, such as medical licenses, board certifications, and proof of education.
- Primary Source Verification: Verifying the accuracy of these documents with the issuing bodies.
- Submitting the credentials to relevant authorities or payer credentialing companies.
- Continuous monitoring to ensure credentials remain up to date.
In the credentialing process for nurse practitioners or doctors, each step is crucial for maintaining compliance with both state and federal regulations, as well as insurance providers.
To enroll in Medicare as a healthcare provider, you must:
- Obtain an NPI
- Have an active state medical license
- Complete the Medicare application and provide supporting documentation, such as your work history and professional liability insurance This process is closely tied to the credentialing process and may require working with healthcare credentialing experts to ensure everything is correctly submitted.



