Effective revenue management is important for the financial health of medical organizations in the changing healthcare industry. At the heart of this intricate process lie two crucial elements: medical billing and coding. Although you might know what is medical billing and coding, this article aims to provide you with deeper insight.
These two components ensure healthcare providers are accurately reimbursed for their services while complying with industry standards and regulations.
This article will explore the nuances of medical billing and coding, their significance, and the challenges healthcare providers encounter in the United States.
What is Medical Billing and Coding?
The importance of accuracy in coding and billing can not be overstated, and plays an integral role in the financial well-being of medical organizations. Gitnux reported that $935 million are lost weekly due to mostly avoidable errors.

Medical Billing
Reviewing Patient Records
They would review the patient's medical records to identify the billable services, including the surgery itself, any associated diagnostic tests, and post-operative care.
Translating Services into Codes
These professionals would then translate the documented services into universally recognized codes, such as CPT (Current Procedural Terminology) codes. For instance, a complex surgery might be represented by a CPT code like "43250" for an esophagogastroduodenoscopy with biopsy.
Claim Submission
Using the coded information, they would prepare a claim that includes all necessary details and documentation required by the insurance company.
Following Up on Claims
After submission, they would diligently follow up on the claim to ensure timely reimbursement. This process may involve communication with the insurance company to address any inquiries or discrepancies.
Medical Coding
Picture a scenario where a physician performs a comprehensive physical examination on a patient. In this instance, the medical coder would assign the appropriate CPT code, like "99214," signifying a detailed office or other outpatient visit.
Imagine a patient is diagnosed with a specific medical condition, such as asthma. The medical coder would use an ICD code, such as "J45.909" for uncomplicated asthma, to categorize and track the condition for statistical purposes.
Let's say a patient requires durable medical equipment like a wheelchair. The medical coder would employ an HCPCS Level II code, such as "E0955," to facilitate billing for the equipment.
Certification in Medical Coding
The Role of Medical Billing and Coding in Revenue Cycle Management
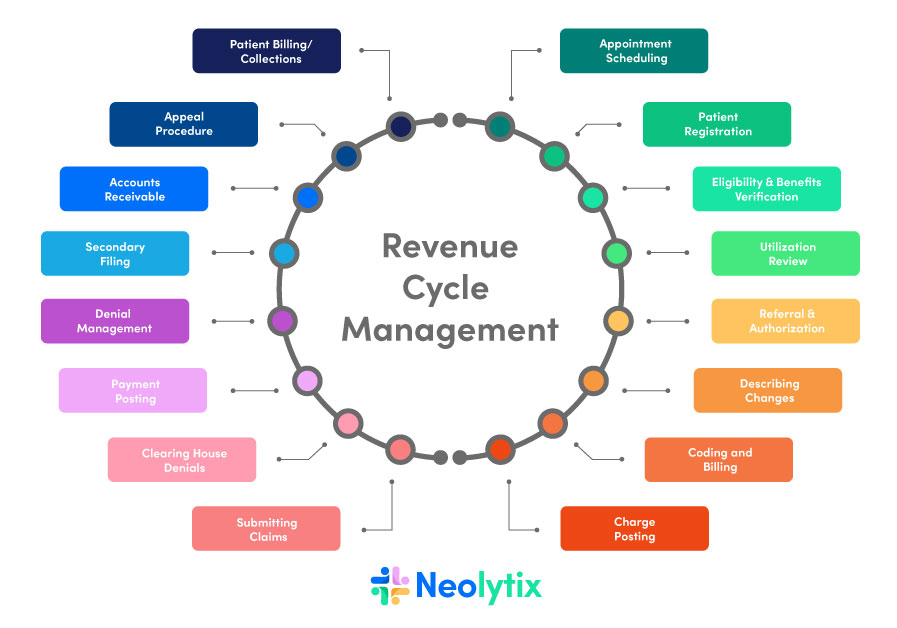
The Billing Process
1. Patient Encounter
To put things into perspective, consider a patient who visits a healthcare provider for a routine check-up. During the visit, the physician performs a range of services, including a physical examination, lab tests, and an electrocardiogram (ECG).
2. Documentation
The healthcare provider meticulously documents all aspects of the patient encounter, recording the findings of the physical exam, the results of lab tests, and the interpretation of the ECG.
3. Coding
Medical coders step in to translate these details into standardized codes. For example, the physical examination may be represented by a CPT code, the lab tests by specific codes, and the ECG interpretation by yet another code. This step ensures that the services provided can be accurately identified and billed for.
4. Claim Submission
Armed with the coded information, a medical biller prepares a comprehensive claim, including all the necessary codes and documentation. This claim is then submitted to the patient’s insurance company for reimbursement.
5. Adjudication
The insurance company receives the claim and assesses it for accuracy and compliance with policy guidelines. They determine the amount they will reimburse the healthcare provider based on the services provided and the patient’s coverage.
6. Payment and Follow-Up
If the claim is approved, the insurance company issues payment to the healthcare provider. However, if there are discrepancies, denials, or other issues with the claim, follow-up actions are taken to address them and ensure that the provider receives the appropriate reimbursement.
The Importance of Accurate Coding
Accurate coding is of paramount importance for several reasons:
- It guarantees that healthcare providers receive proper reimbursement for their services, thus maintaining the financial health of their practices.
- Accurate coding helps prevent claim denials, reducing delays in payment and minimizing administrative burdens.
- Precise coding contributes to accurate record-keeping, essential for patient care and healthcare analytics.
- It aids in compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards, reducing the risk of audits and penalties.
Challenges in Medical Billing and Coding
1. Constant Updates and Evolving Guidelines
Medical coding is not a static field. It evolves constantly to accommodate advancements in healthcare procedures and technologies. Keeping up with these coding changes can be daunting.
Example:
Consider a medical coder responsible for coding procedures for an orthopedic practice. New techniques for joint replacements emerge, and with them, new CPT codes are introduced. Staying current with these updates is essential to ensure accurate coding and billing.
2. Claim Denials and Rejections
Insurance companies frequently deny or reject claims for various reasons, leading to delays in payment and administrative hassles for healthcare providers.
Example:
A healthcare facility submits a claim for a patient’s surgical procedure. However, the insurance company denies the claim, citing a lack of pre-authorization. The healthcare provider must now navigate the appeals process, delaying reimbursement.
3. Complex Coding Scenarios
Certain medical procedures and conditions are inherently complex, making accurate coding a challenging task.
Example:
Imagine a medical coder tasked with coding a complex heart surgery involving multiple procedures. Precision is paramount, as errors could result in underbilling or overbilling, both of which have significant financial implications.
4. Documentation and Information Gaps
Incomplete or inadequate documentation can hinder accurate coding, as coders rely on thorough medical records to assign appropriate codes.
Example:
A patient undergoes a series of diagnostic tests, but the physician’s notes lack specific details about the tests performed and their outcomes. Without complete information, coders may struggle to accurately code the services provided
5. Compliance with Regulations
Healthcare providers must navigate a complex web of regulations, including those related to coding, privacy, and billing practices. Non-compliance can result in penalties and legal issues.
Example:
To protect patient data, a medical billing professional must ensure that billing practices align with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Any lapses in compliance could lead to costly legal consequences.
6. Entry-Level Barriers
Aspiring medical billers and coders often face obstacles in securing entry-level positions due to the preference for experienced and certified professionals.
Example:
A recent graduate with a medical billing and coding certification seeks an entry-level position but finds that most job postings require prior experience. Gaining that initial experience can be a significant hurdle.
7. Technology and Software Challenges
Healthcare facilities rely on complex electronic health record (EHR) systems and billing software, which can be prone to technical issues.
Example:
A medical coder experiences a system outage while working on a batch of claims submissions, resulting in delays and potential errors. Technological challenges like these can disrupt the billing and coding process.
8. Coding Backlogs
High patient volumes and administrative burdens can lead to coding backlogs, where claims are not processed promptly.
Example:
A busy hospital department faces an influx of patients, causing a backlog in coding. This delay can impact cash flow and revenue, as claims are not submitted in a timely manner.
9. Accuracy and Quality Assurance
Ensuring the accuracy of codes and preventing errors is an ongoing challenge, as even small mistakes can have significant financial implications.
Example:
A coding audit reveals that a medical coder consistently assigns incorrect codes for certain procedures. These errors can result in underpayments and costly audits.
10. Staffing and Resource Constraints
Healthcare facilities may face staffing shortages or resource constraints, making it challenging to maintain an efficient billing and coding department.
Example:
A small medical practice struggles to hire and retain skilled billing and coding professionals due to budget constraints. This shortage can lead to a backlog of claims and increased chances of errors.
In conclusion, medical billing and coding are indispensable components of the healthcare revenue cycle, but they are not without their challenges. Healthcare providers and professionals must navigate constant updates, claim denials, complex coding scenarios, and regulatory compliance while ensuring accuracy and quality in their work.
Addressing these challenges requires a combination of expertise, ongoing education, and technological solutions to streamline the process and maintain financial stability in the healthcare industry.
Conclusion
To recap, we’ve explored the intricate medical billing and coding world, from their definitions to their pivotal roles in healthcare revenue cycle management. We’ve also highlighted healthcare providers’ challenges in this arena, underscoring the need for precision and expertise.
Neolytix has been helping healthcare organizations nationwide for over 11 years to improve revenue through improved billing and coding outsourcing and everything else on the administrative side. Benefits of outsourcing to Neolytix include:
- Improve cash flow with faster claims payments and reducing accounts receivable (A/R)
- Reduces administrative burden and operational costs
- Improve in-practice expertise through knowledge transfer
- Decrease revenue leakage by reducing errors and denials
- Save on recruitment and training costs, skilled billing/coding personnel
- Improve compliance and regulatory compliance
- Improve the overall patient experience of a practice
Schedule a no-obligation consultation today to stop revenue leaks and improve your organization’s financial health.



