Table of Contents
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) traces its roots to early telemedicine efforts that began in the mid-20th century. The initial focus was on transmitting medical information over distances, primarily for emergency situations and consultations.
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote monitoring in healthcare as systems sought alternative ways to deliver care while minimizing in-person interactions. In recent years, remote patient monitoring (RPM) has become more popular worldwide.
More people have long-term illnesses. The population is getting older. There is a need for improved healthcare.
RPM in healthcare is expected to grow by 18.2% annually until 2030, making it an essential part of healthcare for better patient care.
What is Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)?
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) is a healthcare technology that allows doctors to monitor patients’ health data from a distance. It uses advanced medical tools to gather current data on vital signs, chronic health conditions, and other important health measurements.
These tools are high-tech and help provide up-to-date information. The information collected includes vital signs, long-term health issues, and other key health measurements. This remote patient monitoring data is then transmitted to healthcare professionals, enabling them to make informed decisions and provide timely interventions.
Before 2020, Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) was not well-known in the medical industry. However, remote patient monitoring for healthcare providers has become more popular because it benefits both patients and providers. This is due to changes in patient preferences and economic factors like the aging population in the US.
In the past three years, the gap between awareness and unawareness of remote patient monitoring has decreased. Misconceptions about remote patient monitoring are also decreasing. However, many healthcare providers still do not understand the differences between remote patient monitoring and telehealth.
RPM vs. Telehealth? What is the Difference?
Remote monitoring healthcare services fall within the broader category of telehealth. RPM is different from telemedicine. Telemedicine is just one part of the larger field of telehealth. Both telehealth and RPM are growing at exceptional rates.
RPM and Telehealth both use technology to care for patients from a distance. However, they differ in their scope, purpose, and the amount of patient data they provide.
RPM focuses on monitoring specific health metrics, while Telehealth offers a wider range of medical services. Additionally, RPM typically collects and analyzes more patient data compared to Telehealth. Research from Future Market Insights and Grand View Research suggests that there is no slowing down in demand for these services within the foreseeable future, as seen below.
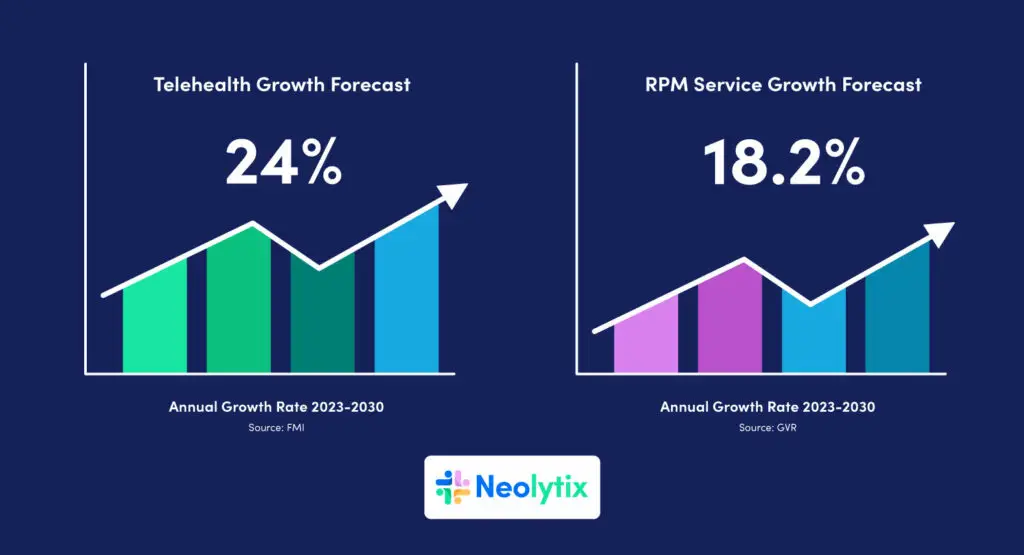
- Telehealth
Telehealth primarily revolves around virtual consultations and remote medical appointments. It allows patients to connect with healthcare providers through video, audio, or text messaging. This mode of care delivery is precious for consultations, follow-up appointments, and providing medical advice.
- Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
RPM goes beyond virtual appointments, delving deeper into continuously monitoring patient’s health conditions and vital signs. RPM gathers live data from medical devices like heart rates, blood pressure, glucose levels, weight, and other important measurements.
This data is then transmitted to healthcare providers, enabling them to gain comprehensive insights into a patient’s health status over time.
Key Differences between RPM and Telehealth | |
Depth of Data | While Telehealth focuses on real-time conversations and medical advice, RPM provides an ongoing stream of physiological data. This allows healthcare providers to track trends, detect anomalies, and formulate informed care plans. |
| Continuous Monitoring | RPM offers a continuous monitoring approach, capturing data at regular intervals or in real-time. Telehealth, on the other hand, is typically limited to scheduled virtual appointments. |
Proactive Care
| RPM empowers healthcare providers to proactively intervene in case of critical fluctuations or abnormal readings. Telehealth interactions are generally initiated by patients seeking medical guidance.
|
Chronic Disease Management
| RPM is particularly effective for managing chronic conditions, where constant monitoring of health metrics is essential. Telehealth is versatile and applicable to various healthcare scenarios.
|
| Personalized Care Plans | RPM’s wealth of data enables healthcare providers to tailor care plans based on a patient’s individual health patterns. Telehealth appointments are more focused on immediate consultations. Additionally, depending on the scope of the service, there are also differences in remote patient monitoring telehealth billing. |
How Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Works
This section outlines how RPM is used. It covers selecting a provider, transmitting data instantly, and enhancing patient care and healthcare outcomes.
- Provider Decision: A healthcare provider or organization chooses to use RPM in their patient care plan. RPM can be utilized to monitor a wide range of conditions, collecting diverse patient data. Common Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Devices include blood pressure cuffs, pulse oximeters, thermometers, glucometers, weighing scales, ECG/stethoscopes, activity trackers, spirometers, and more.
- Patient Consent and Deployment: With the patient’s consent, the provider deploys RPM into the patient’s home or daily life. This deployment is a crucial part of the RPM process. It allows patients to monitor their health from home. This step is important for patients to easily keep track of their health. This is the key part of the process that separates RPM from patient monitoring. RPM focuses on remote and electronic data transmission within patient monitoring.
- Device Setup and Education: Patients are equipped with the necessary devices to collect their health data. They are also provided with education to ensure they understand how to use the technology effectively. This step is important for helping patients take an active role in their care. However, without proper training and confidence, it could affect the success of remote patient monitoring on patient outcomes.
- Vital Monitoring: Once the RPM devices are set up, patients can effortlessly monitor their vital signs. Patients may need to record their vitals daily or more often, based on their condition and the provider’s advice. This flexibility ensures that patient monitoring is tailored to individual healthcare needs.
- Real-Time Data Transmission: The biometric data collected by these devices is sent in real-time to the patient’s healthcare provider. This continuous stream of data allows providers to monitor trends and detect changes promptly. When a reading is abnormal, the provider receives alerts. These alerts help the provider take action for the patient’s health.
Understanding these steps gives a clear picture of how remote patient monitoring works and its impact on improving healthcare outcomes.
Neolytix is an RPM vendor, and in 2023, out of 915 patients enrolled in RPM, 84 red alert readings were received and escalated to reduce potential admissions.

Benefits of RPM for Patients & Providers
RPM is showing more benefits for both providers and patients in the healthcare industry as new research shows its effectiveness.
RPM empowers patients by placing their health management at their fingertips, revolutionizing how they engage with their well-being. Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) has many benefits that help healthcare providers give better, personalized care.
RPM Benefits for Patients
- Convenience and Comfort
- Early Detection and Intervention
- Personalized Care Plans
- Streamlined Follow-Up Care:
- Reduced Anxiety and Improved Quality of Life:
RPM Benefits for Providers
- Enhanced Patient Engagement
- Data-Driven Decision Making
- Additional Revenue
- Timely Interventions
- Improved Reputation
What Devices Are Used for Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)?
RPM relies on advanced medical devices to accurately capture and instantly transmit vital health data to healthcare providers. These instruments are pivotal in transforming healthcare delivery by enabling continuous monitoring of patient’s health conditions.
Cellular RPM uses cell networks to send patient health data from medical devices to healthcare providers. It uses the patient’s cell connection to transmit data even when not near a paired device.
Bluetooth RPM uses Bluetooth technology to send patient data to nearby devices. It is ideal for situations where patients are near a receiving device.
Take a quick look at the most common tools used in RPM. For a more in-depth exploration, check out our article on What is RPM in healthcare and RPM devices.
1. Blood Pressure Monitors
Blood pressure is a crucial indicator of cardiovascular health. Blood pressure monitors, like arm cuffs or wrist monitors, measure systolic and diastolic pressure to give information about heart health.

2. Weight Scales
Weight scales capture weight fluctuations, which can indicate various health conditions. These scales help healthcare providers monitor changes in patients’ weight, aiding in managing conditions like heart failure and obesity.

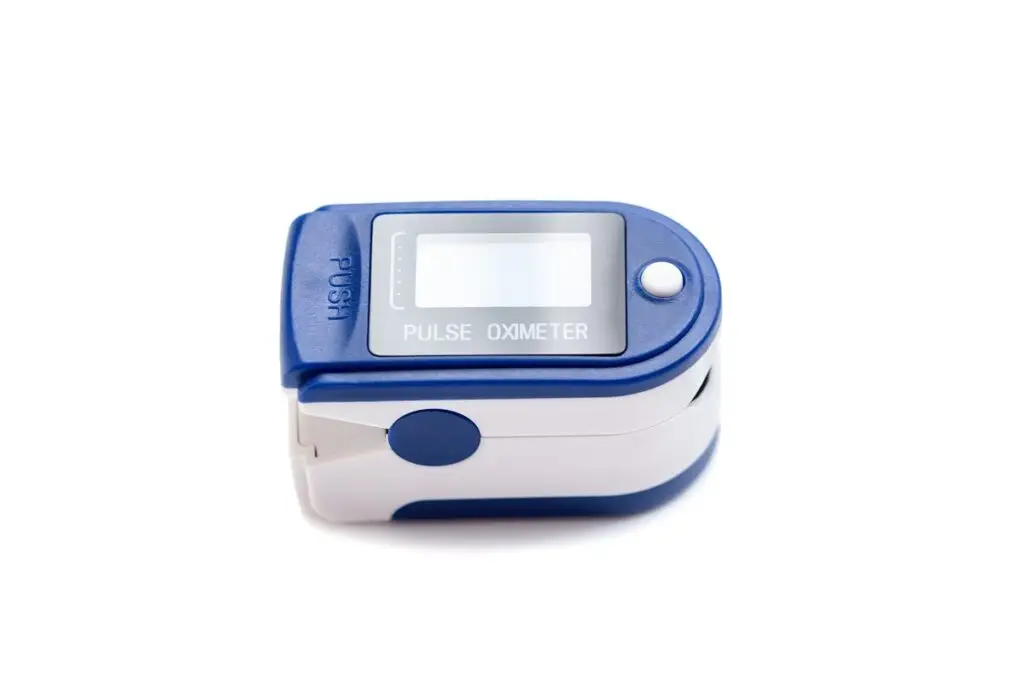
3. Pulse Oximeters
Pulse oximeters measure blood oxygen saturation levels and pulse rates. These devices are particularly valuable for patients with respiratory conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or asthma.
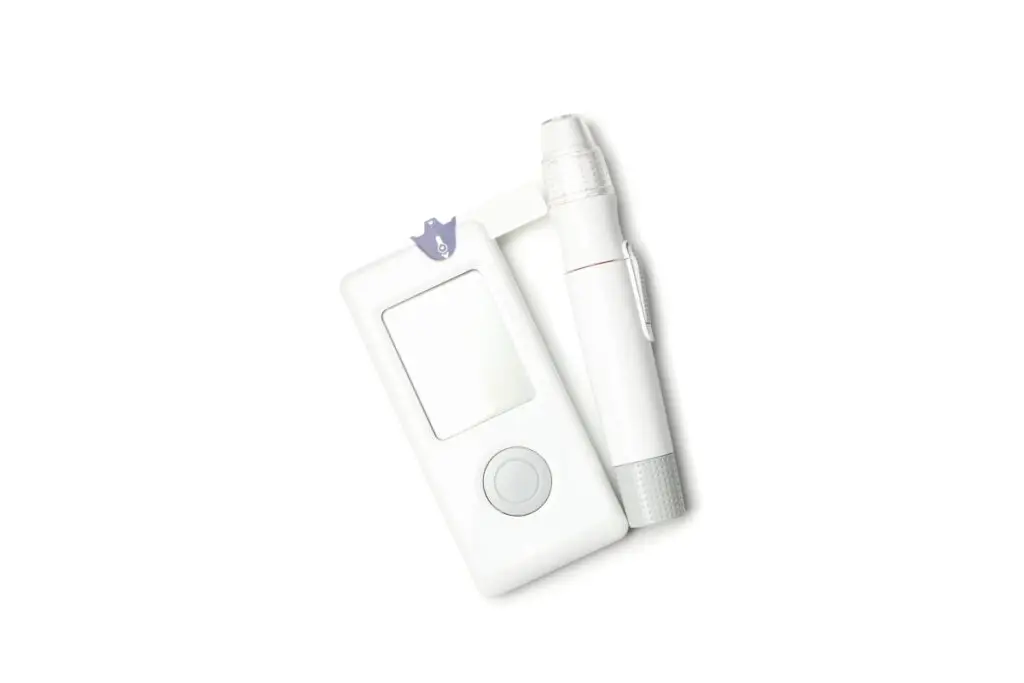
4. Cellular Blood Glucose Monitor
For patients with diabetes, continuous glucose monitoring devices offer real-time insights into blood glucose levels. This is vital for managing insulin doses and preventing complications.
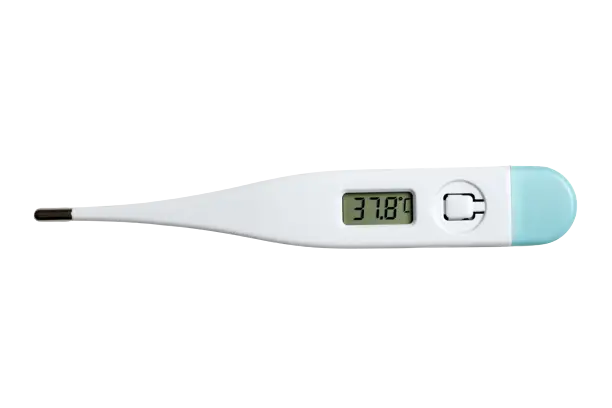
5. Thermometers
Digital thermometers enable patients to monitor their body temperature remotely. This is especially relevant during times when fever can be an early sign of illness.
Other instruments include ECG Monitors, spirometers, wearable health trackers like smartwatches and fitness trackers, and even medication dispensers with RPM capabilities.
For more information on RPM devices, contact Neolytix to schedule a learning session on how these devices can improve patient outcomes.
Overwhelmed or Need Answers Faster?
Medical Conditions Qualifying for Remote Patient Monitoring
RPM holds tremendous promise for improving patient outcomes and quality of life across chronic conditions. RPM transforms the healthcare landscape for patients with regular health challenges by enabling continuous monitoring, early detection, and personalized interventions.
- Diabetes: RPM is invaluable for diabetes management, as it enables continuous monitoring of blood glucose levels. Patients can track fluctuations and receive timely alerts, allowing for prompt insulin dosages and dietary choice adjustments.
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): RPM offers the advantage of regular blood pressure monitoring for patients with hypertension. Any abnormal readings can trigger alerts, leading to timely interventions to prevent complications like heart attacks and strokes.
- Chronic Heart Conditions: RPM is particularly beneficial for patients with chronic heart conditions such as congestive heart failure (CHF). The ability to monitor vital signs like heart rate and weight helps healthcare providers detect signs of worsening heart function and initiate interventions to prevent hospitalizations.
- Chronic Respiratory Conditions: Patients with chronic respiratory conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can benefit from continuous remote patient monitoring of vital signs such as oxygen saturation and lung function. Healthcare providers can intervene early in case of declining respiratory health.
- Chronic Kidney Disease: RPM is vital in managing chronic kidney disease by monitoring blood pressure, fluid levels, and kidney function. Early detection of anomalies allows healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans and prevent the progression of kidney damage.
- Obesity: For patients struggling with obesity, RPM’s continuous monitoring of weight and body mass index (BMI) provides insights into weight fluctuations. This data assists healthcare providers in tailoring weight management plans effectively.
- Neurological Conditions: RPM can benefit patients with neurological conditions like epilepsy by monitoring vital signs and detecting seizures. Timely alerts can help caregivers assist promptly.
- Post-Surgery Recovery: RPM is valuable, allowing healthcare providers to monitor patients’ progress remotely. Any deviations from the expected recovery trajectory can be addressed early, reducing the risk of complications.
- Pregnancy Monitoring: RPM can be applied to pregnancy monitoring, remotely tracking vital signs and maternal health parameters. This approach enhances the care for expectant mothers, especially those with high-risk pregnancies.
- Geriatric Care: Elderly patients with multiple chronic conditions can benefit from RPM’s holistic monitoring. Healthcare providers gain insights into various health metrics, enabling comprehensive care management.
Remote Patient Monitoring Reimbursement: CPT Codes
The Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes provide a standardized system for reporting medical procedures and services, including RPM. Understanding the relevant remote patient monitoring CPT codes is crucial for healthcare providers seeking reimbursement for RPM services.
Here are some key remote patient monitoring CPT codes used for RPM and their implications:
CPT Code 99457 Interactive Communication | CPT code 99457 includes monitoring body functions remotely for at least 20 minutes in a month. This code is used for healthcare providers to talk to patients or caregivers in real-time about monitored data. |
CPT Code 99458 Remote Monitoring Treatment Management | For patients with multiple chronic conditions, CPT code 99458 can be used. It takes clinical staff at least 20 minutes to interpret monitoring data and manage treatment. |
CPT Code 99473 Self-Measured Blood Pressure Monitoring | This code applies to patients who self-measure their blood pressure using an approved device. It covers the initial setup and education for patients on accurate self-measurement. |
CPT Code 99474 Blood Pressure Self-Measurement Management | CPT code 99474 covers ongoing assessment and management of patients’ self-measured blood pressure readings. It includes review and interpretation of the data to make informed treatment decisions. |
CPT Code 99484 Complex Chronic Care Management | For patients with multiple chronic conditions, CPT code 99484 applies. It takes 30 minutes for clinical staff to manage chronic care, including monitoring and communication from a distance. |
CPT Code 99091 Collection and Interpretation of Physiologic Data | CPT code 99091 is used for collecting and interpreting physiologic data that takes at least 30 minutes. This code can be used for remote monitoring of physiological parameters. |
Healthcare providers must accurately record RPM services and use correct CPT codes for billing to get reimbursed. Each code reflects specific aspects of RPM, from initial setup to ongoing management and interactive communication.
Neolytix’s Rev+ Remote Patient Monitoring services offer a symbiotic solution to healthcare organizations keen on introducing RPM in their organizations. Our billing team at Neolytix will make sure you get reimbursed accurately. We only charge a fee for successful reimbursements.
That means your revenue directly affects ours, which is a brilliant motivator for striving toward billing excellence.
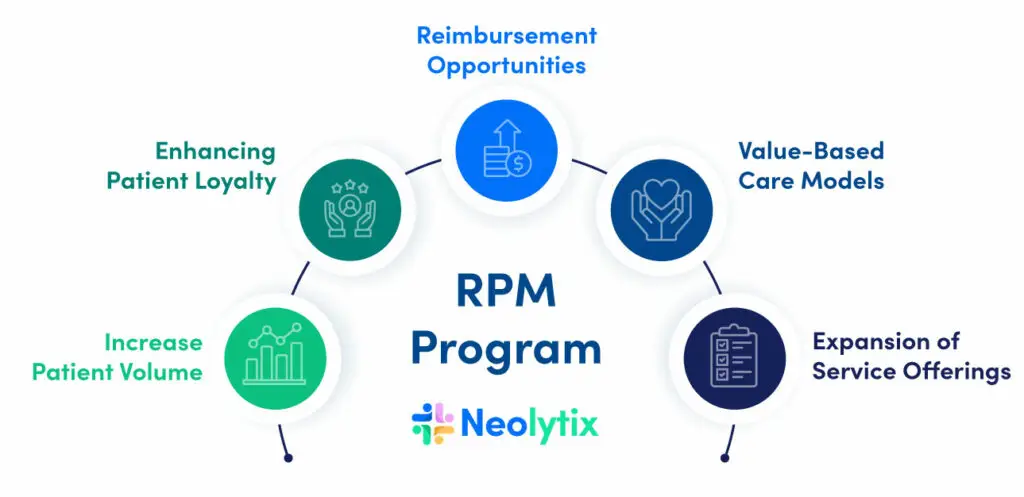
Financial Impact of Remote Patient Monitoring (For Healthcare Providers)
RPM is a catalyst for positive revenue implications in healthcare delivery. By seizing reimbursement opportunities, embracing value-based care, and diversifying service offerings, healthcare providers position themselves for financial success.
- Reimbursement Opportunities: The potential for reimbursement from governments and insurance companies for RPM services is a compelling revenue driver. This aligns with the recognition of the value of remote monitoring in healthcare in preventing costly hospitalizations and complications.
- Value-Based Care Models: The ability of RPM to excel in value-based care models, where healthcare providers are rewarded for delivering improved patient outcomes, holds significant revenue potential. Effective chronic condition management and preventive interventions contribute to financial incentives.
- Expansion of Service Offerings: Diversifying revenue streams by incorporating RPM into service offerings is appealing. Providers can create new service packages catering to patients seeking innovative and comprehensive healthcare solutions.
- Increased Patient Volume: Attracting a more extensive patient base seeking personalized care and continuous monitoring can increase revenue. Word-of-mouth about the benefits of RPM can contribute to higher patient volume and subsequent revenue growth.
- Enhancing Patient Loyalty: RPM’s ability to foster patient engagement and loyalty is a revenue driver. Engaged patients are more likely to return for follow-up appointments, additional services, and ongoing RPM services, positively impacting the provider’s revenue.
Choosing the Right Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Vendor
In a previous article, we discussed the benefits of hiring a remote patient monitoring vendor. We also highlighted the key questions to keep in mind when selecting an RPM vendor.
We suggest reading this article. For now, let’s focus on the top 10 questions to think about when picking an RPM vendor.

Unlock the Benefits of Remote Patient Monitoring
Are you ready to start offering Remote Patient Monitoring services at your healthcare organization?
Take the first step towards redefining patient care and elevating operational efficiency. Schedule a free consultation with Neolytix’s RPM experts. They can explain how RPM can benefit your organization. RPM can help you provide better care, engage patients, and improve financial outcomes.
FAQs
Neolytix RPM solutions streamline patient monitoring through automated processes, lessening the administrative workload for healthcare providers. This efficiency enables clinical staff to concentrate on delivering individualized care and timely interventions.
Patients experience active engagement in their care plans, supported by a dedicated care team closely monitoring their progress and providing assistance as needed.
Absolutely, Neolytix RPM offers blood pressure monitoring as part of its vital signs tracking feature. Monitoring blood pressure is fundamental for effectively managing diverse chronic conditions and maintaining overall patient well-being. Read our comprehensive article about remote blood pressure monitoring to learn more or contact us directly.
Correct. Neolytix will streamline the entire process, overseeing the delivery and replacement of devices. Our team will train and assist patients with device issues. We will also provide technical support to them. Additionally, we will continue to support and follow up with patients.
Zero. Neolytix RPM offers a symbiotic relationship with no up-front costs. We will create a list of eligible users from your existing patients that are eligible for the RPM program. Neolytix will do claims submission and billing for free, and only charge a percentage on successful contracts, making Neolytix RPM a risk-free source of revenue.
Schedule a free consultation to learn more
Complete the form, and someone from our team will contact you!



